REIMAGINE YOUR LABOR COSTS & HR BURDENS
As your offshoring provider in the Philippines, EVES serves as your conduit into a talented, budget-friendly Filipino labor pool.
We recruit exactly the right talent for the specific roles you need to fill, and also house all workforce staff in facilities with:
- A comfortable, air conditioned Western‐standards office
- A blackout‐free environment in a modern building with emergency power generation
- Redundant internet connections with speeds up to 3Gbps
EVES becomes your employer of record, relieving you of all HR administrative burdens & mitigating the need for compliance with costly US federal and/or state regulatory requirements.
Concurrently, EVES takes care of compliance with all local Filipino labor laws.
Offshoring with EVES helps you get work done, increase capacity, improve overall performance, and lower your costs.
CASE STUDIES
CASE STUDIES
What Role Can EVES Help You Fill Today?
ACCOUNTING MANAGER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Accounting Managers supervise accountants, and serve as integral leaders within accounting departments. They apply their knowledge & experience to create systems and processes for analyzing and reporting financial information, ensure organizations follow legal and regulatory requirements, and recommend improvements for business procedures. Accounting Managers oversee teams of accountants working toward an organization’s financial goals, assigning projects and tasks to accountants under their supervision. Accounting Managers also help shape their organization’s accounting policies, priorities, and methods. Many Accounting Managers conduct regular reviews of their division’s processes and systems to identify inefficiencies and improve procedures. They also provide guidance and mentorship to team members.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Manage the month-end close process, including the preparation and review of journal entries.
- Manage the general ledger reconciliation process, including the preparation and review of reconciliations.
- Oversee and prepare month-end financial statements.
- Coordinate year-end audits, tax preparation, and other external reporting requirements.
- Develop and maintain procedural documentation for various accounting functions.
- Train and supervise staff in accounting functions.
- Implement and comply with internal accounting controls in accordance with corporate policies.
- Collect appropriate data and prepare federal, state, and local reports as required. May also prepare and/or review property tax reports and special government reports.
- Design and maintain various required internal and external reports.
- Ensure compliance with US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), federal / state wage and hour rules, and other applicable regulations and company policies.
- Perform special projects, such as analyzing various components of a company’s activities.
- Develop, maintain and update cost analysis models.
- Establish and/or recommend economic objectives and policies to management.
- Oversee financial and operational reporting needs, and assign reports required by regulatory agencies, banks, investors, and other external parties.
- Collaborate in the installation, modification, documentation, and coordination of the implementation of accounting systems and accounting control procedures.
- Analyze, review, and audit company general ledger, accounts payable, and accounts receivable systems.
- Assign duties and monitor quality of work by enforcing company policies, procedures, and government regulations.
- Provide day-to-day guidance and oversight of subordinates and actively work to promote and recognize performance.
- Keep up to date on overall activities of the team, identifying problem areas and taking corrective actions.
- Provide backup coverage for the Controller when unavailable.
- Participate in team meetings. Work collaboratively with other team members to complete projects as assigned.
- Perform ad hoc analysis and projects as requested.
GRAPHICS DESIGNER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Graphics Designers create visual concepts, using computer software or by hand, to
communicate ideas that inspire, inform, and captivate customers. They develop the overall
layout and production design for advertisements, brochures, magazines, and corporate reports.
Leveraging a strong understanding of typography, color, and composition, Graphics Designers
translate an art director’s vision into a compelling visual message, and often collaborate with
copywriters, photographers, and other designers to create a final product.
Graphics Designers must also be able to work within the constraints of a budget and a deadline,
possess excellent communication skills, & most importantly be very creative.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Work on a variety of marketing material across print and digital such as website, email,
PowerPoint presentations, product brochures, white papers, infographics, ads, etc. - Manage and handle workflows from collateral requests and brief creation, to excellent
execution and timely delivery (with or without existing branded templates). - Design event logo/identity, environmental graphics, booths, and related collateral.
- Develop design solutions that are on brand and on strategy to meet client requirements.
- Collaborate with the creative team of strategists, copywriters, art directors, creative
directors, production designers, account managers, & project managers to execute work. - Present work in a compelling way to internal team and external client stakeholders.
- Participate in and/or facilitate design brainstorming and work sessions.
- Proficiency in Adobe Create Suite, Procreate, and other tools for creative professionals.
TREASURER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Treasurers manage money and financial risks for businesses. A corporate Treasurer is often the
right arm of the CFO, helping to develop financial policies and strategies, as well as dealing with
existing and expected cash. Treasurers are responsible for ensuring the availability of the right
amount of cash, at the right time, at the right place, and in the right currency.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Manage daily cash balances and trading in the financial markets.
- Ensure that a company’s cash flow allows it to operate effectively.
- Forecast payments and anticipate challenges from limited cash flow.
- Undertake risk management activities to protect financial well-being.
- Analyze impact of financial markets on performance of products or services.
- Participate in financial projects, such as acquisition of another business.
- Evaluate the financial impact of new business ventures.
- Negotiate loan or overdraft terms with company bankers.
- Create solutions to new financial challenges by applying financial or treasury knowledge.
- Liaise with other departments on a range of issues.
- Provide advice on financial matters impacting the company as a whole.
- Supervise junior members of staff.
- Liaise with bankers and investors to maintain positive working relationships.
- Keep up to date with financial and industry developments.
- Attend board and senior management meetings.
TAX MANAGER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
The Tax Manager’s role is primarily to ensure that an organization’s tax strategy complies with
local, state, and federal tax laws. Tax managers also hold a variety of tax-related responsibilities
that work to minimize their organization’s audit risk. Throughout the year, they prepare and file
their organization’s tax returns, and stay up to date on new tax legislation. Tax Managers focus
on ensuring their organization doesn’t overpay taxes by identifying every available tax deduction
available, as well making sure their organization doesn’t underpay its taxes either.
In the event of an initial public offering, merger, or acquisition, Tax Managers assist by
accurately documenting all transactions from a tax perspective and research/review current tax
laws to ensure everything is accurate and complete for the M&A event.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Facilitate and manage the preparation and review of company federal tax returns and
the accurate, timely filing of all tax forms. - Ensure accurate, timely filing of consolidated federal, state, and local income tax returns
and other business-related filings. - Find and implement opportunities for process improvement in company tax procedures.
- Develop and implement strategic tax planning for all necessary federal and state taxes.
- Manage members of the tax team as they prepare components of the company’s US
federal income tax return and other tax documents. - Plan for and develop overall return calendar and coordinate timing and inputs with tax
team. - Maintain effective control procedures over all aspects of the tax process.
- Manage and facilitate IRS income tax audits: preparing responses, creating schedules,
etc. - Monitor legislative and regulatory tax law developments, communicate the effects of
these developments to management and the tax team, and create strategies to
capitalize on changes to taxation legislation. - Provide support with various internal audits and special tax related projects.
- Review tax returns and quarterly/yearly tax projections.
- Manage and mentor members of the tax team to greater levels of effectiveness and
engagement.
STAFF ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
The Staff Accountant is often responsible for a wide range of accounting and financial tasks,
including preparing journal entries, maintaining ledgers, reconciling bank statements, and
helping to compile financial statements. In addition, they may also be responsible for preparing
tax returns and assisting with audits.
In some organizations, Staff Accountants are also called upon to manage accounts payable and
accounts receivable, and even assist with budgeting.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Prepare monthly balance sheets, income statements, and profit and loss statements.
- Maintain the general ledger.
- Code invoices, set up new accounts, reconcile accounts, and close the monthly books.
- Reconcile bank accounts at least monthly, verify deposits, and address inquiries from
banks. - Reconcile cash disbursement accounts, payroll, customer accounts, and other financial
accounts. - Manage accounts receivable collections.
- Verify and/or complete payment of invoices associated with accounts payable and
ensure payments are charged to the appropriate accounts. - Provide outside auditors with assistance, including gathering necessary account
information and documents to perform annual audits. - File tax forms with federal, state, and local government agencies.
- Coordinate with software vendor to maintain accounting software systems, and
recommend updates to enhance the accounting software. - Manage the purchasing and invoicing system.
- Performs other related duties as assigned.
- Ensure compliance with GAAP principles.
- Stay informed on industry developments and changes in regulations.
COST ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Cost Accountants are stewards of an organization’s financial health, who focus on developing and maintaining effective budgets and costs associated with organizational operations. This may involve examining the organization’s purchases and supply chains to spot areas of improvement or inaccuracies.
Cost Accountants constantly look for new ways to improve the financial health of their employers, using their in-depth understanding of finances, facts, and figures to optimize operations. When they detect inefficiencies, Cost Accountants may need to identify the problem, provide a solution, and possibly even implement or manage the revised processes. Additionally Cost Accountants may concentrate on working with financial investments, government policy, logistics, payroll, benefits, or taxes.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Analyze financial data obtained through studies to determine effects of costs on business.
- Analyze changes in product design, raw materials, manufacturing methods, or services provided to determine effects on costs.
- Provide management with detailed reports for use in making business decisions and controlling expenditures.
- Prepare and analyze standard cost and vendor price comparison of materials to monitor and report on purchase price variances, labor efficiency variances, manufacturing variances, etc.
- Partner with operations and supply chain to highlight potential inventory exposures and recommend resolutions to management.
- Monitor the progress, the completion, and the adherence to company policies of physical inventory counts of finished goods and spare parts. Partner with Corporate accounting and operations to monitor and track capital spending ensuring projects are closed out on-time and in line with budget.
- Prepare (monthly, quarterly and annual) cost forecasts.
- Assist in month-end and year-end closing.
- Prepare and maintain bills of material and assign labor and overhead cost to finished product(s).
- Assist in the accounting month-end process by preparing accrual journal entries, raw material cost allocations, reclassifying operating expenses and distributing manufacturing variances by product and categories.
- Generate and distribute weekly/monthly/quarterly spend, inventory, and production reports as needed.
- Troubleshoot and research unexplained inventory transactions.
- Undertake ad hoc reports and a variety of special ‘one-off’ analytical projects.
- Develop cost standards for labor and burden rates.
- Maintain various records, ad hoc reporting and analysis.
AUDIT SUPERVISOR
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Audit Supervisors are responsible for overseeing the daily operations of the auditing staff,
reviewing and overseeing their work, whether on premise or at external sites. They ensure that
the regulations of the company are being met in the accounting recordkeeping, but depending
on the industry, the Auditing Supervisor also ensures that the company is abiding by federal and
state laws.
The Audit Supervisor constructs audit plans and programs to ensure they are in line with current
auditing standards. Ultimately, the Audit Supervisor is responsible for ensuring that all
accounting and bookkeeping duties, along with auditing duties, are in compliance with the
Corporate Audit Department and Institute of Internal Auditor standards.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Develop annual audit plan and coordinate audit activities.
- Perform audits for business operations, finances, compliance with policies and
procedures. - Oversee audit planning and reporting activities according to established policies.
- Supervise audit team to ensure quality and on-time delivery.
- Evaluate performance of audit staff and provide appropriate feedback.
- Assist in risk assessment and mitigation activities.
- Organize skill development trainings for audit team.
- Review audit findings, & prepare reports with recommendations.
- Assist in developing budgets and timelines for upcoming audits.
- Evaluate current audit procedures and recommend improvements.
- Evaluate and enhance internal controls to improve operational efficiency
- Communicate audit status to management on regular basis.
- Discuss audit observations with management, & make recommendations for
improvements. - Prepare clear and complete audit work papers and store them in departmental
repository. - Analyze and resolve audit issues in a timely fashion.
- Follow changes in regulations and compiling reports regarding compliance issues,
standards, and accounting practices. - Assist the accounting team with other duties.
ASSISTANT CONTROLLER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Assistant Controllers support the controller in the finance or accounting department. They
typically prepare financial statements in accordance with official regulations and are involved in
the implementation of internal controls. Assistant Controllers help with day-to-day operations
and assist in making sure that everything runs smoothly. They may also be called upon to step
into the role of Controller if they’re absent for any reason.
Assistant Controllers also typically participate in annual audits, manage invoices, and ensure
compliance with state and federal accounting laws. Assistant controllers’ duties usually include
reconciling accounts on a quarterly basis, and they must have skills in developing financial
reports for forecasting and reporting.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Prepare and consolidate financial statements and reports.
- Assist with the development and evaluation of budgets and preparing budget reports.
- Support the formulation and implementation of control systems within the organization.
- Oversee accounts payable, accounts receivable, and payroll, identifying discrepancies,
and reconciling accounts. - Support the accounting department with all aspects of the general ledger.
- Ensure strict compliance with company and regulatory standards.
- Prepare and manage accounts using various software programs.
- Prepare and assist with audits, including liaising with external auditors.
- Follow changes in regulations and compiling reports regarding compliance issues,
standards, and accounting practices. - Assist the accounting team with other duties.
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE SENIOR ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Accounts Payable Senior Accountants are responsible for managing the collection of incoming
payments for a company. They prepare official receipts and coordinate with Accounts Payable
Specialists from other companies with pending payables. They ensure that clients pay on time,
and they also follow up on payments when necessary. They are responsible for checking
whether the clients have already paid in full. Accounts Payable Senior Accountants are in charge of
updating accounting records as well to ensure that client records are up to date.
Sometimes they work with Accounts Payable Senior Accountant to balance company financial records.
They maintain knowledge of company bookkeeping policies, audit business ledgers, organize
invoices and begin the collections process for client accounts with past-due balances. Accounts
Receivable Specialists also process and record any unique billing situations that fall outside of
regular operations such as custom payment plans.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Generate timely and accurate customer invoices on a monthly basis.
- Maintain and improve customer contract folders as well as the documentation process
for monthly invoices. - Prepare bank deposits and process all customer payments in the accounting system.
- Monitor accounts receivable aging report to ensure timely customer payments while
communicating with managers to ensure overdue invoices are addressed with
customers. - Assist in resolving customer inquiries regarding invoicing and payment process.
- Assist in reconciling vendor invoices and accurately distributing costs among customers
for invoicing purposes. - Assist in gathering and compiling data to generate monthly revenue reports as well as
other reports relevant to accounts receivable. - Provide support for internal and external audits.
- Perform account reconciliations in a timely and accurate manner.
- Manage collection efforts and associated functions.
- Continually evaluate current policies and make recommendations for process
improvements. - Assist the accounting team with other duties.
- Keep informed of regulatory requirements and best practices in accounting
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE SENIOR ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Accounts Payable Senior Accountant are responsible for the financial processing of transactions for an
organization by overseeing a company’s invoices and ensuring that all bills are authorized,
recorded, and paid in a timely manner. They also make sure the company’s financial records
are current and accurate, including tax information for vendors.
An Accounts Payable Senior Accountant is responsible for obtaining approval from the appropriate
department before submitting a payment and for preparing the payment. They are also the first
point of contact when working with internal and external vendors.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Review invoices for accuracy and proper approvals.
- Match invoices to purchase orders, comparing prices, terms of payment and other
charges. - Ensure bills are paid in a timely and accurate manner or negotiated by their due dates.
- Charge expenses to accounts and cost centers and control petty cash spending.
- Enter transactions to maintain accurate revenue reports.
- Reconcile account transactions with the general ledger.
- Issue purchase order amendments and stop payments.
- Perform bank and credit card reconciliations.
- Assist with the setup of new suppliers.
- Establish and maintain relationships with new and existing vendors.
- Generate monthly, quarterly, or annual statements.
- Assist the accounting team with other duties.
- Keep informed of regulatory requirements and best practices in accounting
ACCOUNTING SUPERVISOR
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Accounting Supervisors work closely with a team of accountants to manage financial functions,
including accounts payable/receivable, bank reconciliations, general ledger reconciliations, and
tax audits. They apply their strong analytical skills to create detailed financial reports and
forecasts. They’re also adept problem-solvers, good team managers who can oversee the work
of junior accounting staff, and ensure financial information is accurate and effective.
The Accounting Supervisor’s responsibilities may include recruiting and training accounting
staff, and instituting disciplinary measures against poorly performing employees. Exceptional
Accounting Supervisors have a sound knowledge of accounting principles and practices, and
are able to keep abreast of the latest developments in accounting technologies and software to
streamline accounting processes.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Oversee daily transactions, including accounts payable/receivable, general ledger and
bank reconciliations. - Perform reconciliations of bank & general ledger accounts.
- Organize financial data into useable information and maintain updated records.
- Analyze financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with generally
accepted accounting practices. - Accurately prepare tax returns and ensure that taxes are paid in a timely manner.
- Participate in regular tax audits and payroll.
- Prepare budgeting reports and forecast revenues.
- Manage month-end, quarterly, and year-end closings.
- Monitor the daily performance of the accounting department.
- Supervise and provide overall guidance to accounting clerks as well as junior accounting
staff. - Track the progress of financial and accounting objectives.
- Identify potential cash flow problems and financial irregularities.
- Provide regular updates to management regarding company finances.
- Liaise with department heads to ensure that each department remains within budget.
- Establish accounting policies and procedures, aligned with company’s targets.
- Ensure compliance with the law.
CONTROLLER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Controllers oversee the accounting operations of a company by leading the accounting team,
and closely monitoring a company’s financial health. They typically maintain, manage, and
analyze financial statements, payroll, budgets, tax compliance issues, and more. Controllers
work across a broad spectrum of industries, for companies both large and small. In a larger
corporate setting, Controllers often supervise a team of accountants and report directly to the
Chief Financial Officer (CFO). In smaller companies, the Controller may be the only accountant,
working with a team of clerks and reporting directly to the owner or CEO.
A Controller is often also expected to develop budgets and forecast future revenues and
expenses. Additionally, Controllers usually must work with other departments to ensure they’re
adhering to the budget. Finally, Controllers also play an important role in shaping the
company’s financial strategy and ensuring that it aligns with the company’s overall business
goals.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Plan, direct, and coordinate all accounting operational functions.
- Manage the accumulation and consolidation of all financial data necessary for an
accurate accounting of consolidated business results. - Coordinate and prepare internal and external financial statements.
- Coordinate activities of external auditors.
- Provide management with information vital to the decision-making process.
- Managing the budgeting process.
- Assess current accounting operations, offer recommendations for improvement, and
implement new processes. - Evaluate accounting and internal control systems.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of accounting software and supporting databases, as needed.
- Develop and monitor business performance metrics.
- Oversee regulatory reporting, frequently including tax planning and compliance.
- Hire, train, and retain skilled accounting staff.
BOOKKEEPER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Bookkeepers are responsible for providing accurate, up-to-date financial information about a
business to help managers make decisions. They manage general accounting ledgers, record
journal entries (transactions), and generate financial statements. Bookkeepers organize, collect,
and store an organization’s financial records, including cash flow statements, bank
reconciliations, and loss statements.
Bookkeepers make it possible for business owners and accountants to build budgets, identify
trends, and plan for the future. Bookkeepers may also share some jobs with accountants, such
as the preparation of annual financial reports and tax returns.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Use bookkeeping software, spreadsheets, and other databases to post up-to-date
financial transactions. - Cross-reference financial transactions against bank statements and other source
documents to confirm accuracy. - Prepare four key financial statements – income statement, balance sheet, cash flow
statement, & statement of changes in equity. - Create and send invoices, and follow up on their payment.
- Ensure invoices from suppliers are accurate and paid in a timely manner.
- Calculate payroll and deductions.
- Follow changes in regulations and compiling reports regarding compliance issues,
standards, and accounting practices. - Assist the accounting team with other duties.
AUDITOR
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Auditors review the accounts of companies and other organizations to ensure their financial
records are accurate and in compliance with the law. They could be inspecting the accounts of
their own employer or those of another organization, and they can also act in an advisory role to
recommend risk aversion measures and cost savings.
Auditors prepare reports detailing their findings for the sake of improving operating procedures
and following certain guidelines, laws, and requirements. Auditors also review their
organization’s accounting systems and account books to ensure their effectiveness and
efficiency, making sure they follow specific accounting procedures.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Perform systematic examinations and appraisals of financial related records, reports,
management controls, and policies and practices which reflect an organization’s financial
condition. - Determine if company accounts, financial control systems, & financial statements are
accurate and in compliance with laws & regulations. - Prepare work papers/reports to document the audit process including audit objectives
and related conclusions, deficiencies, and recommendations for corrective action. - Assist higher level auditors in determining areas of high risk to focus on during an audit,
and other related assigned duties. - Gauge levels of financial risk within an organization.
- Identify if and where processes are not working as they should and advise on changes
to be made. - Compute taxes owed, prepare tax returns, & ensure taxes are paid properly and on time.
- Suggest ways to reduce costs, enhance revenues, and improve profits.
- Follow changes in regulations and compiling reports regarding compliance issues,
standards, and accounting practices. - Assist the accounting team with other duties.
SENIOR ACCOUNTANT – TAX
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Senior Accountant – Tax is responsible for the preparation, analysis, review, and filing of taxes
for individuals and businesses. Additionally, they may also be responsible for conducting audits
and providing tax planning consultation services.
The Senior Accountant – Tax may also assist the tax manager in responding to IRS notices.
When overseeing staff, their other duties include coaching junior tax accountants and being
aware of all compliance issues and deadlines for extensions, tax estimates, required filings, and
more.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Prepare tax returns for individuals and businesses by researching records and applying
tax laws, regulations, and precedents. - Complete audits on companies or individuals to ensure that their financial records are
accurately recorded. - Review financial statements for accuracy and identify any issues that may require
additional investigation. - Provide clients with advice on tax planning strategies to help them reduce their tax
burden in future years. - Maintain tax records and prepare reports for the IRS, state tax agencies, and other
government agencies. - Conduct audits of tax returns to ensure that they are accurate.
- Prepare tax forms, including personal income tax forms such as Form 1040 and
1040EZ, and business tax forms such as Form 1120 and 1120S. - Develop tax strategies for businesses to reduce tax liability.
- Communicate with clients about tax preparation services and filing requirements.
- Compile supporting financial statements and documents.
- Review returns prepared by junior accountants.
- Assist with federal and state tax audits.
- Respond to inquiries from regulatory agencies.
- Perform tax research, staying up to date on new regulations.
SENIOR ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Senior Accountants oversee the work of staff accountants, provide analysis of financial data,
and make recommendations to senior management about how to improve the bottom line.
They are responsible for a wide range of financial tasks, from preparing reports and overseeing
tax compliance to devising budgets and providing advice on financial planning. In large
organizations, Senior Accountants may specialize in areas such as auditing or management
accounting. Regardless of the size of the organization, Senior Accountants are typically involved
in all aspects of financial management.
Senior Accountants also develop and implement accounting policies, provide training and
support to staff accountants, and liaise with external auditors. In addition, Senior Accountants
are often involved in special projects, such as tax planning or process improvement initiatives.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Supervise junior accountants and other staff in accounting department.
- Create and analyze liability, asset, and capital accounts by compiling data and required
documentation. - Summarize and prepare financial status and transactions reports, including profit and
loss statements, and other necessary reports. - Assist the accounting manager in preparing documents and interpreting complicated
financial information for managers, executives, and C-Suite executives. - Comply with all federal, state, and local protocols including legal requirements, and
interpret new and existing legislation. - Create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) manual for accounting policy and
regulations, and roll out reconciliation procedures. - Participate in setting of financial standards and forecast process.
- Develop and document business processes and accounting policies to maintain and
strengthen internal controls. - Assist with audits and taxes.
- Ensure compliance with GAAP principles.
- Stay informed on industry developments and changes in regulations.
PROJECT ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
The Project Accountant is responsible for monitoring the progress of projects, monitoring
budgets, investigating variances, tracking & approving expenses, and ensuring that project
billings are issued to customers and payments collected.
Project Accountants liaise with project managers and other stakeholders as part of their role in
identifying and mitigating financial risks. Occasionally, the Project Accountant may be required
to assist with audits and provide support during the negotiation of contracts.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Review budgets, including staffing, work plans, and fee structures.
- Provide project managers and clients with timely financial reports and budgets, as well
as project forecasts. - Prepare pre-billing reports for project managers to review.
- Prepare actual costs, working capital, and tax reports.
- Monitor receivable income and support project managers with collections.
- Review and approve time sheets for work related to a project.
- Review and approve overhead charges to be applied to a project.
- Issue invoices and purchase orders, as well as paying consultant, subcontractor, vendor,
and supplier bills. - Ensure a steady cash flow by generating, auditing, and sending invoices in a timely
manner. - Update contracts according to client requirements and reporting associated budget
amendments. - Create project accounts in the accounting system & close them out upon project
completion. - Maintain project-related records, including contracts and change orders.
- Investigate project variances and submit variance reports to management.
- Compile information for internal and external auditors, as required.
PAYROLL SUPERVISOR/MANAGER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
The Payroll Supervisor/Manager is responsible for overseeing the payroll department and
ensuring the accurate and timely processing of employee payroll. This includes ensuring that all
employee information is up to date and accurate, calculating hours worked and withholdings,
and processing payroll on time. In addition, the Payroll Supervisor/Manager may be responsible
for preparing reports and analyzing data related to employee compensation.
In many organizations, the Payroll Supervisor/Manager is often tasked with providing customer
service support to employees regarding their pay and benefits. The Payroll Supervisor/Manager
also maintains compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Oversee procedures and processes, and manage inquiries and requests related to
preparation and distribution of payroll. - Implement, maintain, and review payroll processing and accounting systems to ensure
timely and accurate processing of payroll transactions including salaries, benefits,
garnishments, taxes, and other deductions. - Ensure accurate and timely processing of payroll updates including new hires,
terminations, and changes to pay rates. - Maintain or oversee the maintenance of employee records.
- Ensure compliance with federal, state, and local payroll, wage, and hour laws and best
practices. - Facilitate audits by providing records and documentation to auditors.
- Identify and recommend updates to payroll accounting software, systems, and
procedures. - Perform other duties as assigned.
PAYROLL ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Payroll Accountants are responsible for ensuring that employees are paid accurately and on
time. They maintain payroll records, calculate taxes and deductions, and prepare reports. In
addition, they may also be responsible for administering benefits, such as medical insurance
and retirement plans.
In larger organizations, Payroll Accountants may supervise a team of clerical staff. The Payroll
Accountant must also ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations, and
occasionally are also called upon to maintain employee records.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Implement, maintain, and review payroll processing and accounting systems to ensure
timely and accurate processing of payroll transactions including salaries, benefits,
garnishments, taxes, and other deductions. - Ensure accurate and timely processing of payroll updates including new hires,
terminations, and changes to pay rates. - Prepare and maintain accurate records and reports of payroll transactions.
- Ensure compliance with federal, state, and local payroll, wage, and hour laws and best
practices. - Facilitate audits by providing records and documentation to auditors.
- Identify and recommend updates to payroll accounting software, systems, and
procedures. - Perform other duties as assigned.
JUNIOR ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Junior Accountants typically perform entry-level accounting and bookkeeping tasks, but often
assist Senior Accountants with financial reports, maintaining ledgers, and preparing tax returns.
In smaller organizations, Junior Accountants may also be responsible for managing general
ledger accounts, updating financial statements, maintaining accounts receivable and accounts
payable, and paying monthly payroll.
In larger organizations, Junior Accountants may also be called upon to oversee inventory or
handle customer inquiries. Occasionally they assist with auditing and budgeting as well.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Post and process journal entries to ensure all business transactions are recorded.
- Update accounts receivable and issue invoices.
- Update accounts payable and perform reconciliations.
- Assist in the processing of balance sheets, income statements, and other financial
statements according to legal and company accounting and financial guidelines. - Assist with reviewing of expenses, payroll records, etc. as assigned
- Update financial data in databases to ensure that information will be accurate and
immediately available when needed. - Prepare and submit weekly/monthly reports.
- Assist senior accountants in the preparation of monthly/yearly closings.
- Assist with other accounting projects.
INTERNAL AUDITOR/MANAGER
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
The Internal Auditor/Manager is responsible for examining the financial records of the
organization and assessing the reliability of financial reporting. The Internal Auditor/Manager
also evaluates the effectiveness of the organization’s internal controls and makes
recommendations to improve them. In addition, the Internal Auditor/Manager provides
assurance that the organization is complying with applicable laws, regulations, and its own
standards.
The Internal Auditor/Manager also provides guidance on how to improve organizational
efficiency and effectiveness, as well as provides assurance to management and the board
about the adequacy of the organization’s risk management and control processes. Occasionally
the Internal Auditor/Manager may also be involved in investigating fraud or irregularities within
the organization.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Objectively assess a company’s IT and/or business processes.
- Assess the company’s risks and the efficacy of its risk management efforts.
- Ensure that the organization is complying with relevant laws and statutes.
- Evaluate internal control and make recommendations for improvement.
- Identify shortfalls or gaps in processes.
- Promote ethics and help identify improper conduct.
- Assure safeguards.
- Investigate fraud.
- Communicate findings and recommendations to appropriate management.
- Provide an opinion (Unqualified, qualified, adverse, or disclaim).
FORENSIC ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Forensic Accountants analyze, interpret, summarize and present complex financial and
business-related issues in an effort to uncover financial fraud. They work closely with law
enforcement agencies and attorneys to build cases against individuals or organizations
suspected of white-collar crimes.
Along with testifying in court, a Forensic Accountant may be asked to prepare visual aids to
support trial evidence. For business investigations, forensic accounting entails the use of tracing
funds, asset identification, asset recovery, and due diligence reviews.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Investigate and analyze financial evidence.
- Develop computerized applications to assist in the analysis and presentation of financial
evidence. - Communicate findings in the form of reports, exhibits, and collections of documents
- Assist in legal proceedings, including testifying in court as an expert witness and
preparing visual aids to support trial evidence. - Stay informed on industry developments and changes in regulations.
FIXED ASSET ACCOUNTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
The Fixed Asset Accountant is responsible for all aspects of the organization’s fixed assets,
including acquisition, disposal, valuation, and accounting. In addition, the Fixed Asset
Accountant must maintain accurate records of all transactions and ensure that all assets are
properly accounted for in the financial statements.
Fixed Asset Accountants must also be able to maintain accurate records and perform audits
when necessary. In addition, the Fixed Asset Accountant regularly communicates with other
members of the accounting team and provides timely reports on the status of assets. The Fixed
Asset Accountant plays a vital role in ensuring the accuracy of the company’s financial
statements and provides valuable insights into the company’s operations.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Create and monitor a system of controls, procedures, and forms for the recording of
fixed assets. - Recommend to management any updates to accounting policies related to fixed assets.
- Assign tag numbers to fixed assets.
- Record fixed asset acquisitions and dispositions in the accounting system.
- Track the compilation of project costs into fixed asset accounts, and close out those
accounts once the related projects have been completed. - Reconcile the balance in the fixed asset subsidiary ledger to the corresponding
summary-level account in the general ledger. - Calculate depreciation for all fixed assets.
- Review and update the detailed schedule of fixed assets and accumulated depreciation.
- Calculate asset retirement obligations for those fixed assets to which AROs are
applicable. - Investigate the potential obsolescence of fixed assets.
- Conduct periodic impairment reviews for intangible assets.
- Conduct periodic physical counts of fixed assets.
- Recommend to management whether fixed assets should be disposed of.
- Conduct analyses related to fixed assets as requested by management.
- Prepare audit schedules relating to fixed assets, and assist the auditors in their inquiries.
- Prepare property tax returns.
- Represent the company during any audits by a government that involve fixed assets.
- Track company expenditures for fixed assets in comparison to the capital budget and
management authorizations. - Stay informed on industry developments and changes in regulations.
CREDIT ANALYST
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
A Credit Analyst is responsible for assessing the financial stability & creditworthiness of
individuals and businesses. This includes reviewing financial statements, evaluating debt-to-
income ratios, and considering other factors such as job stability and asset ownership to identify
any risk factors. In addition to making recommendations about whether or not to extend credit,
Credit Analysts also determine the terms of the credit, such as the interest rate and the length of
the repayment period. Credit Analysts typically work in banks or other financial institutions.
However, some may also work for companies that provide credit information or for businesses
that are seeking financing.
The job of a Credit Analyst is important in helping to prevent defaults on loans and other debts.
A Credit Analyst may also be assigned the role of reviewing the credit limits of existing
customers to determine if they qualify for an increase in their credit limit. The analyst will assess
the borrower’s repayment history, earnings information, as well as any history of defaulting on
credit in making their determination.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Evaluate credit data and financial statements in order to determine the degree of risk
involved in lending money or extending credit to individuals or businesses. - Prepare reports detailing the degree of risk in lending money or extending credit to
clients. - Analyze client records and use the data to recommend payment plans.
- Confer with credit associations and references to exchange credit information on clients.
- Help supply chain and sales and marketing departments in managing financial orders to
help them control credit exposure, make payments on time, and reduce the risk of
customer disputes. - Confer with clients to verify their financial/credit transactions and to resolve their
complaints. - Enter, update and retrieve information for credit applications.
- Ensure that all approved applications comply with bank criteria.
- Review deals involving junior Credit Analysts and assist them as needed.
- Assist with bank and client audits.
- Stay informed on industry developments and changes in regulations.
EXECUTIVE/VIRTUAL ASSISTANT
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
Executive/Virtual Assistants offer administrative support for you and your business. They
typically handle tasks such as scheduling appointments, making phone calls, arranging travel,
or organizing emails. Some Executive/Virtual Assistants handle clerical and bookkeeping tasks,
while others may post regular updates to social media or write articles for a blog.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Coordinate, schedule, and confirm calls and appointments.
- Play the ‘bad cop’ to protect your time from people trying to sneak onto your schedule or
give you their sales pitch. - Send and maintain a “pending list” of people who haven’t responded to requests for
setting up a meeting or a call. - Keep significant others informed when you will be unavailable or even out of town.
- Screen emails by deleting, responding, forwarding, or flagging them for your attention.
- Add, update, and delete people to your contacts list or CRM tool.
- Transcribe voicemails, and highlight important action items for follow up.
- Research & book travel arrangements, by screening flights that meet your criteria, based
on airline loyalty awards, seat preferences, etc. - Research & book hotels, including ensuring your preferences are met, finding discount
rates, etc. - Research & book ground transportation options, including rental cars, rideshares, trains,
and even public transportation. - Research leads on LinkedIn (or other websites) and create a list of prospective clients.
- Help recruit employees by screening prospective job candidates on LinkedIn based on
criteria you provide. - Perform basic bookkeeping such as maintaining your books, reviewing transactions, and
doing monthly reconciliations. - Create and send invoices to clients & follow up on payments.
- Make purchases by shopping online and saving you time in finding what you need.
- Research and send gifts to clients, prospects, and people in your personal life.
- Fill out online forms such as subscribing to SaaS products.
- Conduct research on just about anything.
- Set up projects in your project management system, invite the appropriate participants,
and even delegate tasks on your behalf. - Handle file management, ensuring files are put in the right place with the right filename,
and that the right people have access, whether it’s on Dropbox, Google Drive,
SharePoint, or elsewhere. - Schedule social media posts across all platforms, including LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook,
Instagram, Reddit, etc. - Proofread and edit letters, blogs and presentations.
CPA
DESCRIPTION OF ROLE
CPAs are responsible for providing financial guidance to organizations in a variety of settings. In
addition to preparing and reviewing financial statements, CPAs may also be involved in attest
services, tax planning, auditing, internal controls, forensic accounting, & management
consulting. The specific duties of a CPA vary depending on an organization’s needs, but they all
require a high level of analytical and mathematical skills.
CPAs often need to interpret complex financial data and use it to make sound recommendations. They must also be able to communicate effectively with both clients and co-workers. CPAs may also be called on to advise clients on mergers and acquisitions, business valuations, litigation support services, and other financial matters.
TYPICAL DUTIES
- Organize and update financial records as needed (digital and physical).
- Perform regular, detailed audits to ensure accuracy in financial documents, expenditures
and investments. - Forecast revenue and analyze profit margins.
- Analyze transactions and prepare reports.
- Oversee ledger reconciliation and manage accounts payable/receivable.
- Publish audited financial statements.
- Participate in budgeting processes.
- Brief senior managers regularly on the company’s financial status.
- Liaise with tax accountants to track tax payments and returns.
- Monitor bookkeeping activities regularly.
- Establish accounting policies and procedures.
- Audit individual accounts on a random or scheduled basis.
- Work with executives and CEOs to establish budgets.
- Make suggestions regarding budgets and other financial decisions.
- Oversee Accountants and other financial professionals.
- Assist with external company audits.
- Stay informed on industry developments and changes in regulations.
EVES PROVIDES ALL THE INFRASTRUCTURE YOUR STAFF NEEDS TO BE PRODUCTIVE

WELCOME!

A typical EVES workstation with comfortable ergonomic chair, modern desktop PC, & an uninterruptible power supply.

Every workstation is assigned dual monitors to provide EVES staff with extra screen real estate that minimizes the need to open & close windows, so productivity is maximized.

A typical workstation cluster in the newly expanded section of our office.
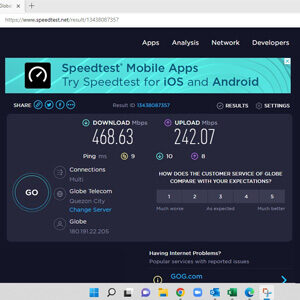
EVES has redundant internet connections from two different providers to ensure uptimes, with speeds up to 3Gbps (currently pictured speed test reflects speeds throttled back to 500Mbps).

The office building has a robust backup power generator installed that makes sure productivity is never sacrificed due to storms or other outage-causing events.
“Instead of using 3 different offshoring providers in the Philippines, we’re consolidating all our hiring with EVES. We find their in-person work to be much more effective.”